
Throughout the educational journey of the vast majority, there exists a glaring deficiency in the realm of monetary education. The conventional curriculum pervading our universities is deeply entrenched in the Keynesian economic doctrine—a doctrine I’ve personally come to recognize as nothing short of pseudoscientific sophistry, devised to legitimize the governmental stronghold over currency creation and distribution. This approach fundamentally distorts the essence of economic principles. True economic logic dictates that production precedes consumption, a tenet starkly contradicted by Keynesianism, which advocates for the stimulation of production through an increase in consumption.
In this article, I’ll dive deep into the basic principles of Bitcoin and the upcoming Bitcoin halving which will occur on April 21. This event occurs every four years with Bitcoin. While it is very simple to essentially understand, it has profound ramifications for Bitcoin and understanding the how, and why, Bitcoin has been the best performing investment of all time.
This Keynesian philosophy endorses the notion the mere act of printing money can magically provide shelter and sustenance for the populace. It propagates the fallacy that economic recuperation and the resolution of societal woes can be achieved through the proliferation of fiat currency. Such thinking is fundamentally flawed. Keynesianism simplifies economic recovery to a matter of monetary expansion, suggesting that problems can be ‘solved’ by flooding the market with more money.
However, when one peels back the layers of complexity shrouding this topic, adorned with convoluted terminology and intricate financial lingo aimed at bewildering the layperson, the truth about money becomes starkly clear. To draw a simple analogy, the act of printing money equates to thievery. It dilutes the value of the currency held by savers, surreptitiously siphoning off their purchasing power and reallocating it to those who are first in line to the printing press. This phenomenon, known as the Cantillon effect, has profound ramifications on the distribution of wealth, serving to exacerbate inequality.

It’s high time we scrutinize and challenge the widespread acceptance of Keynesian economics, recognizing it for what it truly is: a doctrinal guise for economic manipulation and control. From a monetarist perspective, inflation arises primarily from an excessive increase in the money supply, far outpacing the growth of real goods and services in the economy. This phenomenon, often likened to a hidden tax, silently erodes the purchasing power of individuals’ savings and income, acting as a form of stealthy theft. By diluting the value of money, inflation benefits those closest to the monetary spigot—the government and certain financial institutions—at the expense of the general public, who are left to grapple with the diminishing value of their hard-earned money. This redistributive effect underscores the importance of stringent monetary policies focused on maintaining stability in the money supply to protect the economy from the insidious effects of inflation. Milton Friedman famously stated, “Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.” He emphasized that inflation results from an increase in the money supply that outpaces economic growth, underscoring the importance of controlling the money supply to manage inflation.
When we study economics one of the most observable truths that we encounter is that inflation is baked into traditional economic thought and planning. Citizens are taught to anticipate that the cost of goods and services will be greater in the future, primarily because the purchasing power of money has perpetually decreased over time. Over the long term this has horrific consequences for the poor and economically illiterate who become victims of “higher prices” of goods and service.
Let me make an analogy that is very relevant for stock traders. Whenever an investor invests in a company, their ownership is very clearly defined by comparing the totality of the number of shares they own to the totality of shares issued by the company. As investors, we would never accept the idea of an elastic stock certificate. It represents a scenario where a shareholder could unilaterally increase their ownership stake in a company at the expense of other investors by simply issuing themselves more shares. This idea of an “elastic stock certificate” suggests a mechanism where a shareholder could inflate their ownership stake arbitrarily, disregarding the rights and interests of other investors. Such a concept would undermine the integrity and stability of the financial markets, erode investor confidence, and violate securities laws and regulations. However, this is exactly what monetary authorities do when they manage the money supply. They create more currency out of thin air and dilute the purchasing power for anyone using that currency.
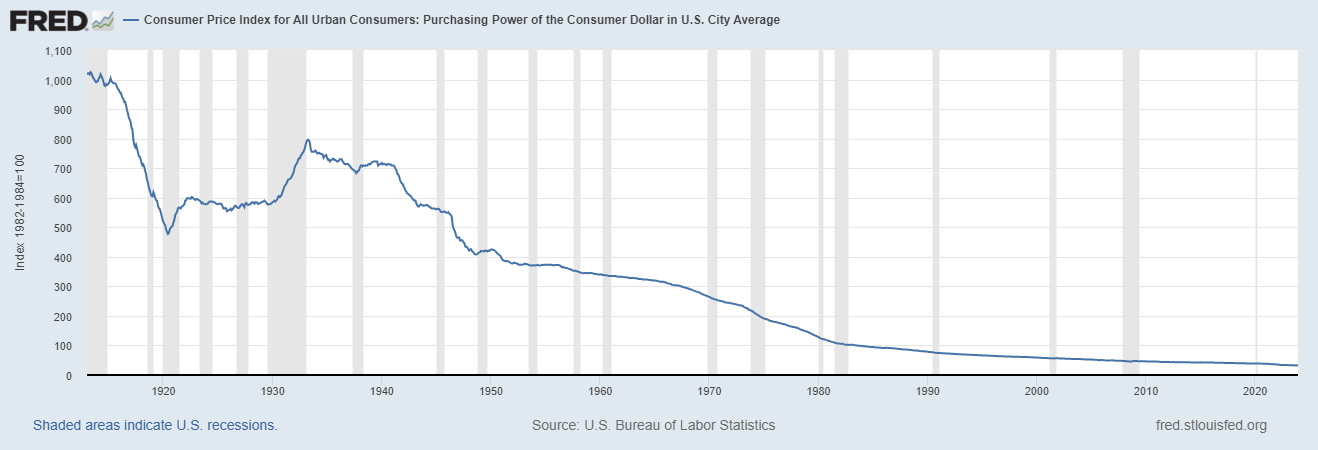
Look at the following chart which displays the purchasing power of the dollar since the Federal Reserve was established. In the last 111 years the U.S. dollar has lost almost 98% of its purchasing power. This unfortunate reality is defended by proponents who believe that government must debase the currency to govern. Philosophically this logic anticipates numerous contradictions which appear to justify theft by our leaders in the name of the common good.
This debate has become center stage with the advent of bitcoin which challenges the notion of nation states monopolistic control of money.
Bitcoiners recognize that Inflation disproportionately benefits debtors, particularly those with fixed-rate borrowings, and entities close to the monetary creation source, such as governments and financial institutions. These beneficiaries gain from the reduced real value of their debts as inflation diminishes the purchasing power of the money they must repay, effectively reducing the real burden of their obligations. Conversely, the most adversely affected are savers, fixed-income earners, and retirees, who find the value of their savings and incomes eroded by rising prices. This erosion of purchasing power represents a wealth transfer from savers to borrowers, and from the public to those with direct access to the newly created money. As such, inflation acts as a regressive tax, hitting hardest those least able to absorb its impacts, undermining the value of savings and fixed incomes, and widening the economic divide between different societal groups.
These principles are important to understand whenever you discuss or seek to understand bitcoin because while bitcoin is money, it is a peaceful revolution against the status quo. Bitcoiners are trying to build a new paradigm in the digital age that is transparent, secure and allows value to transfer between participants without the need of any third-party intermediaries. There’s a large integrated belief in the world that inflation is necessary for a productive economy. Bitcoin challenges that assumption.
Bitcoin represents the pinnacle of financial technology, a revolutionary form of money that leverages cryptography and a decentralized network to offer something entirely new: a secure, transparent, and limited form of currency unlike anything before it. If private property is the power for an owner to control an asset independent of anyone else’s actions, then Bitcoin is the strongest form of private property that human beings have ever had.
Its foundation lies in blockchain technology, a digital ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. This ensures that Bitcoin is not only secure from fraud and theft but also operates independently of central authorities like governments and banks, which traditionally control and issue money.
Bitcoin represents not merely a form of currency, but rather, it embodies money encased within the impregnable fortress of military-grade encryption. This foundational design renders it invincible, a testament to the ingenuity behind its creation, ensuring that the notion of halting its march forward is beyond the realm of possibility. But to view Bitcoin through the narrow lens of finance alone is to miss the vastness of its potential.
We stand on the brink of a monumental shift, a reimagining of the digital landscape as we know it. Bitcoin is the catalyst for this transformation, promising a future where digital monopolies crumble under the weight of a newly democratized platform. It heralds the end of an era dominated by censorship, ushering in an age of unfettered communication protocols that leverage the unassailable nature of Bitcoin.
This is the thrill of our current epoch – the realization that Bitcoin is so much more than a currency. It is the architecture upon which the digital age will be rebuilt, a foundation for a world where information flows freely and power is redistributed back to the individual. Through Bitcoin, we glimpse the future: a society liberated from the constraints of traditional monopolies and censorship, empowered by an unstoppable protocol that guarantees the integrity and accessibility of information for all.
One of the most groundbreaking aspects of Bitcoin is its strict limit of 21 million coins. This scarcity is coded into its very fabric, ensuring that no more than this number can ever be created. This finite supply starkly contrasts with fiat currency, the government-issued money that most people use daily, which can be printed in unlimited quantities. Over time, governments and central banks tend to print more money to manage economic issues, such as to stimulate spending during a recession. However, this can lead to inflation, where the value of money decreases as more and more of it floods the economy, diminishing its purchasing power.
The value proposition of Bitcoin, therefore, lies in its immunity to such debasement. Unlike fiat currencies, which can lose value over time due to inflation, Bitcoin’s capped supply mimics the scarcity of precious metals like gold, traditionally seen as a hedge against inflation. This scarcity can make Bitcoin more attractive as a long-term store of value, especially in times of economic uncertainty or when people lose faith in traditional financial systems’ stability.
Bitcoin is often hailed as the most technologically advanced and sophisticated form of money ever created, offering a unique combination of security, transparency, and scarcity. Its revolutionary approach to currency, with a fixed limit of 21 million coins, presents a stark alternative to the perpetually inflatable nature of fiat currency, positioning Bitcoin as a digital form of “gold” for the modern era. This intrinsic scarcity and technological prowess underpin Bitcoin’s value proposition, making it a compelling option for those looking to diversify their assets beyond traditional fiat currencies.
Let’s unravel the enigma that is Bitcoin, juxtaposed against the backdrop of our traditional payment mechanisms.
Picture this: a typical day, you saunter into a store, ready to make a purchase with your bank card. The routine is almost muscle memory. Your card details are handed over, a silent, digital query flies through the ether to your bank, probing whether your account’s coffers are ample enough to sanction the purchase.
The bank, the omnipotent keeper of ledgers, affirms your solvency, and like clockwork, your transaction sails through. Your account diminishes by the purchase amount, while the vendor’s account burgeons, minus a sliver claimed by the bank for its role as the financial sentinel.
Enter the visionary, Satoshi Nakamoto, who gazed upon this daily dance of transactions and posed a revolutionary question: How do we excise this banking intermediary yet safeguard the sanctity of the transaction? Until the advent of Bitcoin, such a feat was relegated to the realms of fantasy.
Nakamoto’s stroke of genius was to dismantle the central bastion of trust, the bank, and forge in its stead a decentralized ledger, the blockchain, a tome not of one, but of every computer in the network’s domain. These digital auditors, known as “miners”, stand guard over the integrity of transactions, rewarded in bitcoin for their vigilance. Through a symphony of consensus, these miners validate and authorize transactions, etching them into the blockchain. This decentralized consensus mechanism is Bitcoin’s bulwark against counterfeiting, while it simultaneously emancipates financial interactions from the clutches of central authority.
To truly grasp the seismic shift Bitcoin heralds, one must appreciate the quintessence captured in five simple words, a mantra that embodies the disruptive spirit and revolutionary potential of this digital currency.

These attributes are what define the Bitcoin network which consists of millions of computers spread across the world who are responsible for validating transactions in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
In a world dominated by the fluctuating policies of central banks, such as the U.S. Federal Reserve, which wields the power to inject or withdraw currency from circulation based on economic tides, the conventional framework of monetary management stands in stark contrast to the digital frontier introduced by Bitcoin. Traditional monetary levers, employed to steer economies away from recession or to cool down inflation, hinge on the ability to manipulate the supply of money—increasing liquidity by purchasing securities or tightening it by selling them off.
However, Bitcoin emerges as a paradigm shift from this norm, embodying a vision that is both revolutionary and immutable. Its core, a supply schedule etched into the very code that binds its network, represents a departure from the malleable policies that underpin fiat currencies. This rigid blueprint, far from being a limitation, is a testament to Bitcoin’s foundational principle: a currency with a capstone of 21 million units, unyielding to the whims of human governance or political maneuvering.
This deliberate scarcity, a concept foreign to the endless possibility of printing more money characteristic of state-backed currencies, bestows upon Bitcoin its intrinsic value. By design, Bitcoin is insulated from the inflationary pressures that plague traditional currencies, ensuring that its worth is influenced not by policy changes but by its utility and the finite limit of its existence. In this light, Bitcoin is not just an alternative to the dollar or euro; it is a reimagining of what currency can be in an age where digital innovation reshapes our economic landscapes.
Bitcoin represents nothing short of a seismic shift in computer science, introducing a groundbreaking framework that ensures verification and trust among disparate parties over the inherently insecure and mistrustful environment of the internet. The genius of Bitcoin lies in its ability to enable the safe, secure, and verifiable transfer of digital property from one internet user to another, fundamentally changing how transactions are conducted. This system ensures that only the asset’s owner can initiate a transfer, and only the intended recipient can accept it, with the transaction’s integrity open for validation by any observer. Remarkably, Bitcoin achieves all this at a fraction of the cost imposed by traditional intermediaries such as banks, which have long profited from their roles as trusted authorities.
In our increasingly digital society, where the vast majority of payments traverse the web, mediated by middlemen—whether credit card companies like Amex, Visa, and MasterCard, digital payment platforms such as PayPal, GooglePay, and Apple Pay, or online services like WeChat in China—the move towards digital payments has inherently meant a reliance on central entities to approve and verify every transaction. This shift from tangible cash, which individuals can physically manage, transfer, and verify independently, to digital bits managed and authenticated by third parties, invites reflection on the true cost of such convenience.
Through this lens, Bitcoin is not merely a cryptocurrency but a beacon of hope for a future where financial transactions are democratized, liberated from the clutches of centralized authorities. Its emergence challenges us to reconsider not just the mechanics of our monetary transactions but the very fabric of societal control and freedom in the digital age.
Bitcoin’s issuance schedule is the integral aspect of its design, aimed at creating scarcity and controlling inflation. Here’s a breakdown of the bitcoin issuance schedule from its inception until the last bitcoin is mined:
**Genesis Block (2009): ** Bitcoin was launched by an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto on January 3, 2009. The initial block, known as the genesis block, contained a reward of 50 bitcoins.
**Halving Events: ** Bitcoin’s issuance rate is halved approximately every four years in an event known as a “halving.” This is hardcoded into the protocol and is aimed at reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are created, thus controlling inflation.
The first halving occurred in November 2012, reducing the block reward from 50 to 25 bitcoins.
The second halving occurred in July 2016, reducing the block reward from 25 to 12.5 bitcoins.
The third halving occurred in May 2020, reducing the block reward from 12.5 to 6.25 bitcoins.
The fourth halving will occur on April 21, reducing the block reward from 6.25 bitcoin to 3.125 bitcoins.
The fifth halving will occur in April 2028
The sixth halving will occur in April 2032
The seventh halving will occur in April 2036
The eighth halving will occur in April 2040
The ninth halving will occur in April 2044
After each halving, the number of Bitcoin issued per block decreases by half. This reduction continues until all 21 million Bitcoin are mined on February 4, 2140.
Once this limit is reached, no more Bitcoin will be created, and miners will rely solely on transaction fees as incentives for validating transactions on the network.
In summary, the Bitcoin issuance schedule follows a predetermined pattern of halving the block rewards approximately every four years until the last bitcoin is mined, which is projected to occur around the year 2140, leading to a total supply cap of 21 million bitcoins.
This issuance schedule is front and center for every bitcoiner because it presents the central tenet of economics as the most important economic reality. If demand remains constant when supply falls, prices must rise, (number go up!).
The principles of supply and demand stand as the foundational concept in economics, encapsulating the intricate dynamics of market interactions. At its core, it delineates the delicate balance between the availability of goods and services (supply) and the desire or need for those products (demand).
Understanding the dynamics of supply and demand holds profound implications across all sectors of the economy. Policymakers rely on this framework to formulate effective economic policies, aimed at achieving desirable market outcomes. Businesses utilize supply and demand analysis to set prices, allocate resources efficiently, and gauge consumer preferences, thereby enhancing their competitiveness in the marketplace. Investors leverage this understanding to make informed decisions regarding asset allocation and market trends, maximizing their returns while minimizing risks. Consumers benefit from the insights provided by supply and demand analysis, enabling them to make rational choices based on price signals and product availability.
The implications for traders and for money in general are quite profound. Bitcoin has only been around since January 2009. In that time frame, without a marketing department, CEO or customer service department it has revolutionized financial markets and captivated the imagination of developers and entrepreneurs.
The phenomenon of halving captures the collective imagination, fueling speculation and debate over its potential impact on price. This event, marked by a reduction in the rate at which new bitcoins are generated, stands as a testament to the currency’s deflationary design. While many anticipate that this scarcity will naturally drive-up value, the reality is always cloaked in uncertainty.
To date, Bitcoin has undergone three such halvings, each serving as a historical marker from which we can attempt to glean insights. Yet, in this digital age where the future often unfolds in unpredictable ways, these precedents offer no guarantees. They are, instead, chapters in an ongoing narrative that continues to challenge our understanding of value, scarcity, and the very fabric of financial systems.
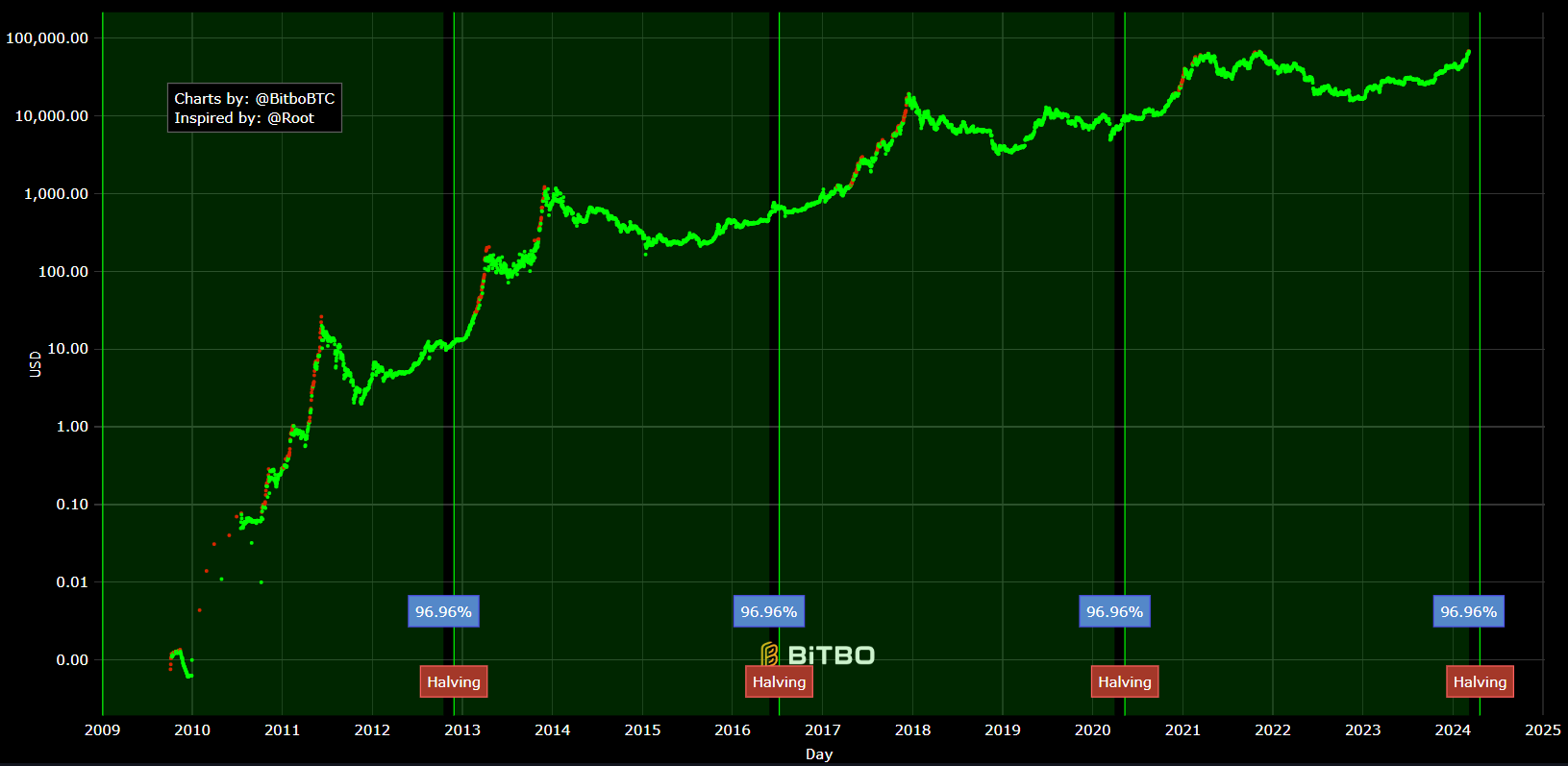
Here is a logarithmic chart showing all the bitcoin halvings so far. Upon studying it you will see why bitcoiners are so excited. Should the future resemble the past, the probabilities greatly favor a significant increase in price.
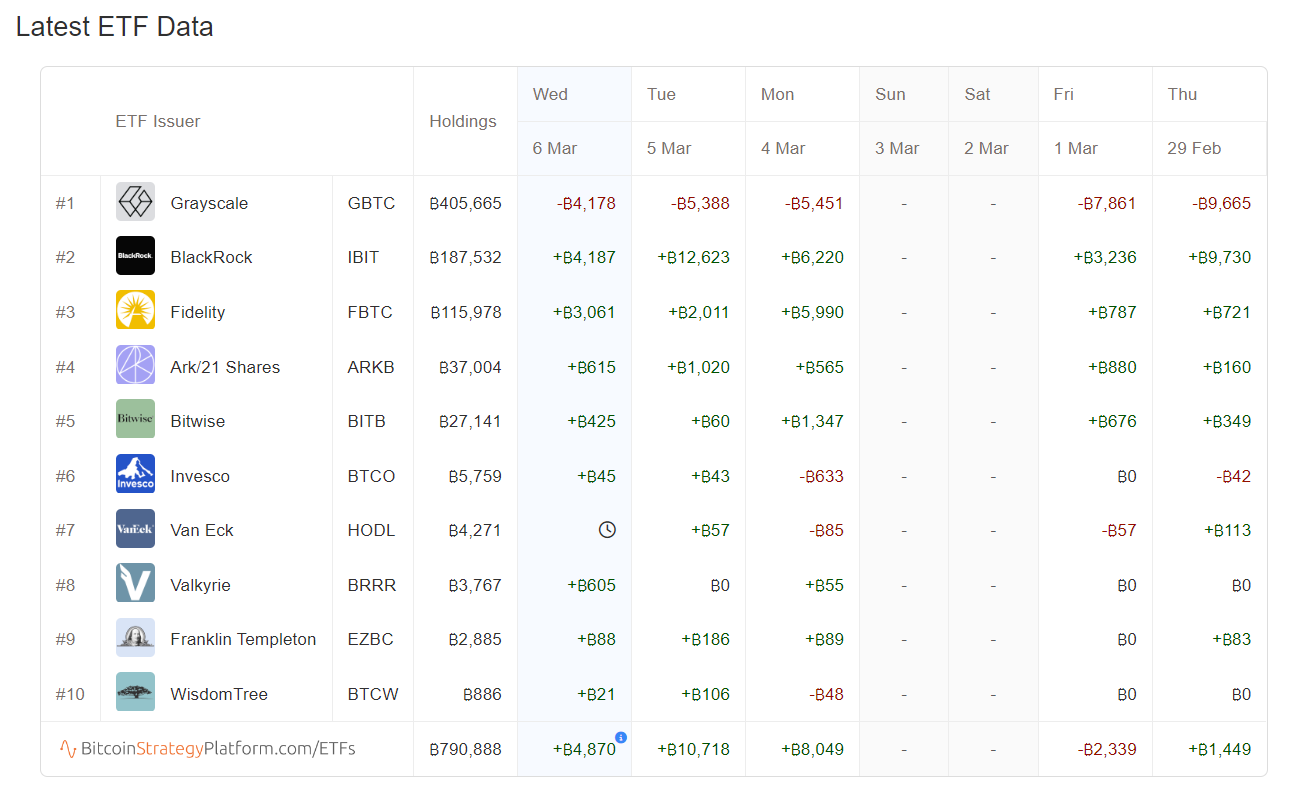
One of the events that has occurred in 2024 is the approval of the Bitcoin ETF. Currently there are 11 companies that have received the green light from the SEC to be allowed to accept funds to invest in Bitcoin.
A great resource that you can bookmark to see how much bitcoin these companies are acquiring is BitcoinStrategyPlatform.com. The BITCOIN ETF was approved on January 11, 2024. Since then, these combined 11 ETF’s have gone on to purchase a total of over 790,000 bitcoin. Since only 900 bitcoin are produced daily and that amount will be cut by 50% over the coming weeks, it certainly feels like a massive bull run is in order.
In an era where economic headlines often spell uncertainty, Bitcoin emerges as a beacon of potential, heralding a new chapter in financial systems amidst the digital revolution. This is not merely about transitioning from old to new; it’s about reimagining possibilities in a world where technology has leveled the playing fields in unprecedented ways. From 2008 to 2023, we’ve observed a stark dichotomy within the financial landscape, revealing deep-seated inequities that underscore our systems.
Consider the contrast between the financial elites, with their hedge funds, IPOs, and venture ventures, who have enjoyed an 87% surge in stock values post-inflation, and the average American saver, whose bank savings have dwindled in real value by 45%. This scenario paints a vivid picture of a system skewed towards the affluent, where the rich see exponential growth in their investments, while the working-class individual watches their savings’ purchasing power halve.
This economic disparity goes beyond numbers; it’s a reflection of lives affected, dreams deferred, and a growing chasm between the haves and have-nots. It prompts a crucial discourse on why the economic equilibrium has tilted so drastically towards the privileged few, leaving the majority to grapple with the erosion of their financial security.
Accountability for this systemic oversight seems elusive, with the current economic rhetoric normalizing a 2% annual loss in purchasing power as an acceptable compromise. This gradual conditioning to higher prices underpins a significant shift in consumer behavior and perceptions of value, subtly but profoundly altering our relationship with money and commodities.
The narrative of economic recovery, often championed by indicators like GDP growth and employment rates, misses a critical evaluation of the quality and impact of such activities. Government spending, distinguished from private economic endeavors, often lacks direct relevance and utility for the average citizen, raising questions about the efficacy and intention behind such expenditures.
In the realm of trading, the emergence of artificial intelligence as a pivotal tool underscores the evolution of market analysis and decision-making. A.I.’s capacity to sift through the noise and focus on the underlying market drivers offers traders a nuanced perspective, emphasizing the importance of discernment in a landscape rife with information overload.
Let me explain. If you watch Bitcoin for any period of time you will hear all of the most outlandish forecasts in the history of forecasting. Just this year I have heard prominent individuals say it was going to several million dollars while others proudly proclaim that it is going to zero.
Folks, when you’re in the trading trenches, remember this: the only scorecard that counts is how well you’ve nailed those price predictions. All that noise you hear, the endless chatter on financial networks, the so-called experts, and their market gossip – it’s just a sideshow to the real action.
I neither have the horsepower nor bandwidth to validate long term forecasting. Instead, I rely on the power of artificial intelligence to clearly define the trend. Look at the following chart which leaves no questions unanswered regarding what the trend was at any given time.
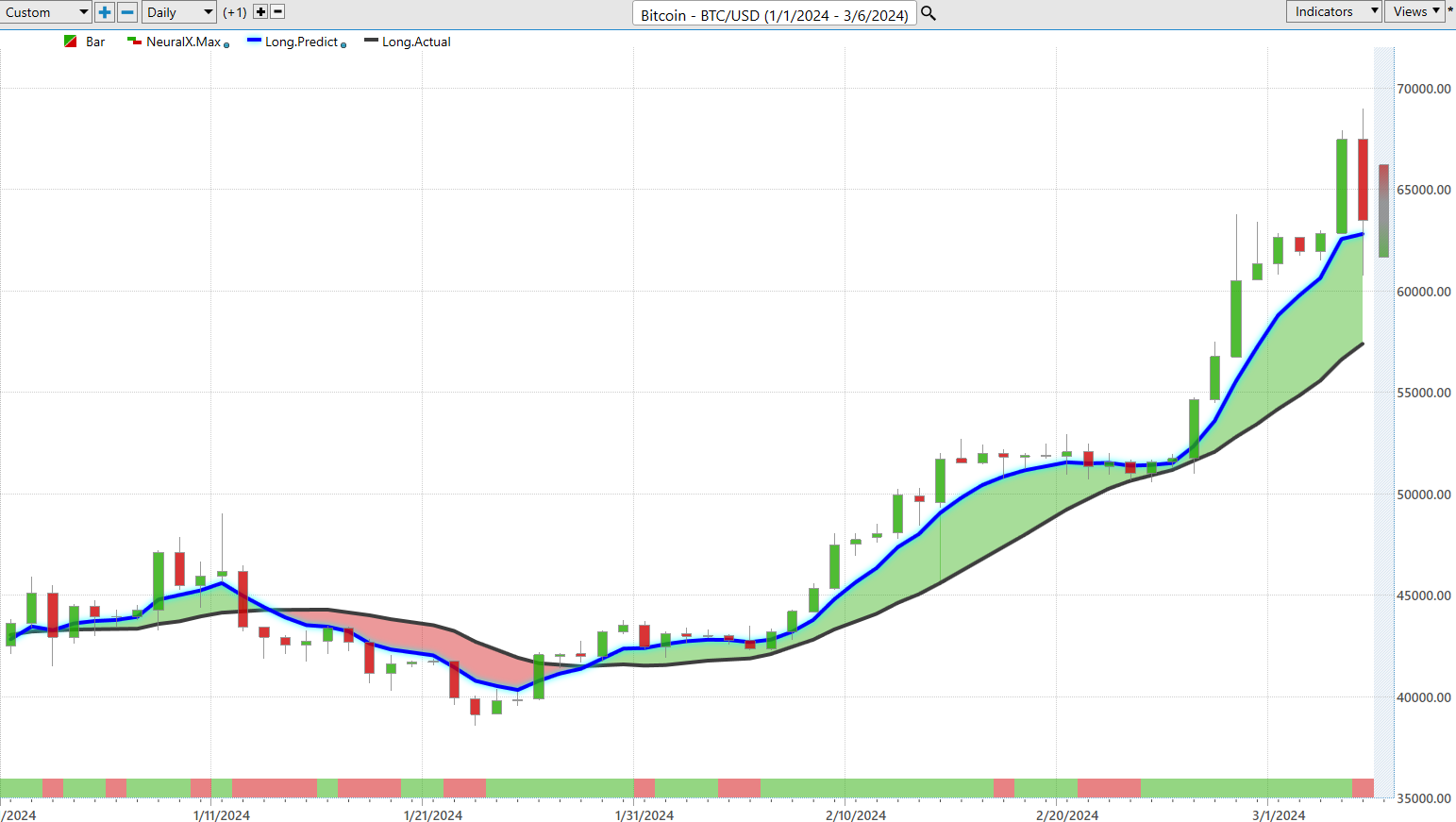
While Wall Street hangs on to every word of the daily financial circus, the savvy trader ought to be homing in on the pearls of wisdom that artificial intelligence trading brings to the table. These aren’t just number-crunching gadgets; they’re the market’s heartbeat, slicing through the chaos of daily headlines, getting to the heart of what truly moves those markets.
For traders, the compass should be as clear as day: up, down, or sideways.
Everything else? It’s a mere distraction. Navigating these waters requires more than gut feeling; it’s about harnessing the power of AI trading software as your North Star, guiding you through the unpredictable twists and turns of market trends, elevating your trading game.
The race to debase is a reality that hits everyone right in the gut. The only question worth asking is what are you going to do about it?
We delve deep into these topics in our no-cost trading master classes, where we impart the wisdom of trading with artificial intelligence , machine learning, and neural networks.
To explore the transformative potential of AI in trading, I invite you to join us for a FREE Live Training session .
Discover how A.I. can help you minimize risk, maximize rewards, and provide peace of mind in your trading journey. Don’t miss this opportunity to equip yourself with the knowledge and tools that can make all the difference.
It’s not magic.
It’s machine learning.
Make it count.
THERE IS A SUBSTANTIAL RISK OF LOSS ASSOCIATED WITH TRADING. ONLY RISK CAPITAL SHOULD BE USED TO TRADE. TRADING STOCKS, FUTURES, OPTIONS, FOREX, AND ETFs IS NOT SUITABLE FOR EVERYONE.IMPORTANT NOTICE!
DISCLAIMER: STOCKS, FUTURES, OPTIONS, ETFs AND CURRENCY TRADING ALL HAVE LARGE POTENTIAL REWARDS, BUT THEY ALSO HAVE LARGE POTENTIAL RISK. YOU MUST BE AWARE OF THE RISKS AND BE WILLING TO ACCEPT THEM IN ORDER TO INVEST IN THESE MARKETS. DON’T TRADE WITH MONEY YOU CAN’T AFFORD TO LOSE. THIS ARTICLE AND WEBSITE IS NEITHER A SOLICITATION NOR AN OFFER TO BUY/SELL FUTURES, OPTIONS, STOCKS, OR CURRENCIES. NO REPRESENTATION IS BEING MADE THAT ANY ACCOUNT WILL OR IS LIKELY TO ACHIEVE PROFITS OR LOSSES SIMILAR TO THOSE DISCUSSED ON THIS ARTICLE OR WEBSITE. THE PAST PERFORMANCE OF ANY TRADING SYSTEM OR METHODOLOGY IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS. CFTC RULE 4.41 – HYPOTHETICAL OR SIMULATED PERFORMANCE RESULTS HAVE CERTAIN LIMITATIONS. UNLIKE AN ACTUAL PERFORMANCE RECORD, SIMULATED RESULTS DO NOT REPRESENT ACTUAL TRADING. ALSO, SINCE THE TRADES HAVE NOT BEEN EXECUTED, THE RESULTS MAY HAVE UNDER-OR-OVER COMPENSATED FOR THE IMPACT, IF ANY, OF CERTAIN MARKET FACTORS, SUCH AS LACK OF LIQUIDITY. SIMULATED TRADING PROGRAMS IN GENERAL ARE ALSO SUBJECT TO THE FACT THAT THEY ARE DESIGNED WITH THE BENEFIT OF HINDSIGHT. NO REPRESENTATION IS BEING MADE THAT ANY ACCOUNT WILL OR IS LIKELY TO ACHIEVE PROFIT OR LOSSES SIMILAR TO THOSE SHOWN.

