Trader sentiment can be used as a contrarian indicator across financial markets. Trading with sentiment may also assist investors in determining directional biases and possibly even finding potential trends in markets.
This article will provide an explanation of what stock sentiment analysis is, examples of sentiment indicators and how this kind of analysis can be applied when analyzing stocks.
What is Sentiment Analysis in the Stock Market?
Stock sentiment analysis can be used to determine investors’ opinions of a specific stock or asset. Sentiment may at times hint at future price action . This is also an example of how trading psychology can affect a market, assisting as a forecasting tool to determine possible future price changes in a particular asset.
There are various factors that influence stock sentiment, which include news (economic, political and industry related) and social media. These factors help influence stock sentiment as they impact stock market volatility , trading volume and company earnings .
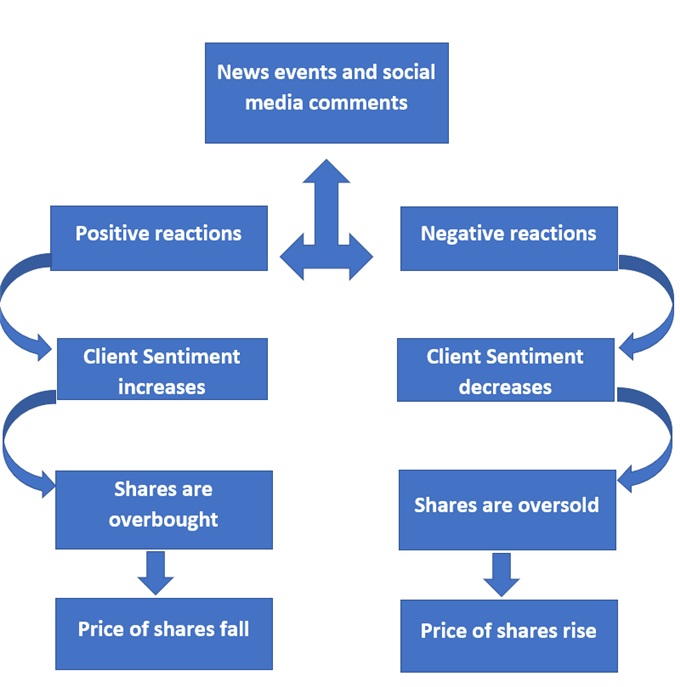
Can Sentiment Help Traders Anticipate Changes in Stock Prices?
Stock sentiment alone cannot always predict changes in share prices , but when combined with tools such as technical analysis , a better understanding can be gained to determine possible scenarios.
In periods of high volatility, stock prices can be much more susceptible to rapid changes. Certain informational and emotional events, such as negative comments on Twitter/social media and news, may cause fear in the market and push investors to overwhelmingly sell a specific share or company. The opposite can also be true when positive news is released, which may translate into optimism and perhaps boost the price of a given stock. That initial rush of fear or excitement, creating outsized moves in the market can quickly create overbought or oversold conditions.
For example, in February 2018 social media influencer Kylie Jenner tweeted the following:
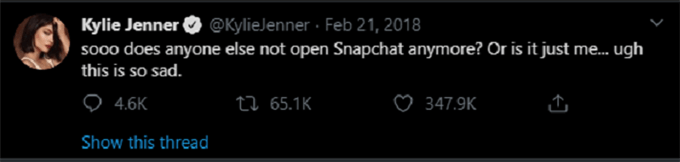
With over 39 million followers, it’s not surprising that this tweet appeared to have a large impact on the share price of SNAP, the parent company of Snapchat. Within a day, the share price decreased by 7% and SNAP lost approximately $1.3 billion in market value.
When technical factors reach extreme readings, traders may begin to see a reversal as more likely. The same can be perceived when sentiment is at extreme levels. For example, if 90% of retail clients are long a specific market or stock, this could potentially be seen as a bearish signal.
Using Sentiment Indicators to Trade Stocks
Sentiment indicators are typically used to determine whether a market is “bullish” or “bearish”. When investors predict that the price of a stock will increase, they may purchase the share and if enough investors do the same - sentiment could be deemed bullish. Likewise, when investors think the price of a share can decrease and act as such by selling the stock, then sentiment may be seen as bearish.
The most common sentiment indicators are:
- Put/Call Ratio
- Volatility Index
- Client Sentiment
1) Put/Call Ratio
To understand put/call ratios, one needs to understand what an option is. A stock option gives traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a stock at an agreed-upon price (the strike price) on a specified future date. Options are often used by investors to hedge or reduce risk exposure of their portfolio.
There are two flavors of options, call options and put options. A call option is the option to buy a security at a pre-determined price (strike price) by a pre-determined date (expiration). Conversely, a put option is an option to sell at a pre-determined price by a pre-determined date. Investors that are bullish in a stock may look at buying call options to take advantage of the higher prices that they’re expecting; while an investor that’s bearish may look at buying a put option, so that when the stock price falls they can later sell the stock at the higher strike price of the option.
The put/call ratio refers to the volume of put options to call options on a given security. The result of the put/call ratio can be used to gauge the sentiment for a given stock. For example, if 9,000 traders have bought call options for Apple Inc and 1,000 traders have bought put options in the same trading session, then sentiment would be seen as bullish as a majority of investors appear to expect the price of Apple to increase.
The put/call ratio can be calculated for any security that has tradable options contracts.
2) Volatility Index
The CBOE Volatility Index ( VIX ) represents market expectations of implied volatility – or anticipated price fluctuation – in the S&P 500 over a period of 30 days. Unlike the put/call ratio explained above, the VIX is forward-looking.
The VIX tends to increase when traders expect share prices to fall and decreases when traders expect prices to rise. In other words, there is often a negative correlation between the VIX and the US benchmark stock index.
Put options tend to have a higher weighting than call options since investors frequently use options as a hedging tool to protect their portfolios against potential changes in stock prices. When the demand for put options increases, this can lead to an increase in the VIX, which is one of the reasons why many refer to it as the ‘fear gauge’.
3) Client Sentiment
Client sentiment data is derived from retail traders and indicates the percentage who are long or short an asset at a given time. This data can indicate when positioning is approaching extreme ends relative to the price of the asset in question. This is part of how sentiment analysis is referred to as a contrarian indicator.
provides client sentiment data which is based off live IG retail client trades for forex , commodities, cryptocurrencies and major stock indices . However, stock sentiment analysis is also available for individual shares on the IG platform.
Stock Market Sentiment Analysis: Key Takeaways
- Trader sentiment can be used to determine hidden trends in the stock market
- Client sentiment can be beneficial when combined with other analytical tools
- Sentiment may indicate when positioning is approaching extremes relative to the price
- IG Client Sentiment (IGCS) shows how many are going long or short, the percentage change over time and whether market signals could be bullish or bearish
Further Readings on Trading with Market Sentiment
- For more information about IG Client Sentiment, read our trading using sentiment article
- Discover how to read ‘risk-on’ and ‘risk-off’ sentiment
- Learn how sentiment analysis can be used to trade forex
Stock Market Sentiment FAQs
What does it mean to be bullish or bearish in the stock market?
To be bullish a stock means that the trader expects the price to rise. Likewise, if an investor thinks the stock could fall, then they are perceived as bearish.
What is the impact of negative sentiment on stocks?
The impact of negative sentiment could lead to an increase in traders looking to sell the share. When sentiment is negative, it likely means that investors are pessimistic about the value of the stock and this could lead to it being oversold, at which point reversal potential may appear from oversold conditions, thereby leading to the potential contrarian implementation of sentiment analysis.

